Modern Immunology
Immunology is a study of about how the body identifies foreign bodies and reacts to them. In essence it is the study about the body's self defense mechanisms. The word "immunology" came from Latin "immunis", which was originally a law concept, and means "not subject to an obligation imposed on others"; e.g. immune from taxation. At first, immunology concentrated on studying anti-infection aspects only, which belonged to a branch of microbiology. In the 1960's, the rapid advancement of immunology expanded to include non-infectious aspects, such as autoimmune, allergy and immunodeficiency, consequently it became an individual science.
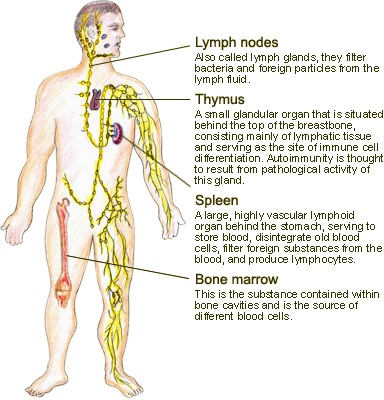
According to modern theory, the body depends on the immune system to fight against various infections from bacteria, microbes, viruses, toxins and parasites. It also clears up harmful materials inside our own body. The whole process can be understood as self-discrimination and elimination of foreign bodies in an attempt to create an internal equilibrium and provide physiological protection for the body. Thus, when the immune system is normal, health can be maintained. On the other hand, when the immune system is malfunctioning, disharmony will occur and give rise to illness. The above functions are carried out by an integrated body system, which includes organs (thymus, spleen and lymph nodes), tissues (skin and mucosal layers), cells (lymph cells and macrophages) and cell products (immunoglobulin, antibodies and complement).
To sum it up, the human immune system has three basic functions: defense, surveillance and homeostasis.
| The Immune Organs of the Body |
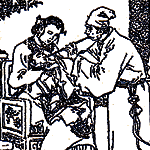 |
| The variolation method in ancient times: the patient inhales the vaccine powder through the nose with the aid of a silver tube. |
TCM immunology has its own unique characteristics listed below:
The concept of holism is a main characteristic of TCM immunology.
From the beginning, TCM has employed holistic approaches; because, it sees the human body as an organic whole. The correlations between the organs and tissues, as well as the human person and the living environments, are organized according to specific orders, which give rise to mutual balance between each physiological function. This integral stability and harmony is the root of disease defense and health maintenance. Any disturbances in this equilibrium will cause disease. Every part of the body such as qi (vital energy), blood, body fluids, organs and the meridians has its own particular function. They combine to build up the body's defense system and bring out their protective strength mutually. According to TCM concepts, the body's natural resistance against diseases and its repair ability are described as a flow of energy that circulates throughout the body, which is called the healthy energy (zheng qi).
Healthy energy (zheng qi) is the integral manifestation of the human body's immune functions.
Under normal circumstances, the body depends on the immune system to fight against various infections and to clear up harmful materials in order to keep a clean internal environment. When the immune system functions normally, health can be maintained; otherwise disharmony will occur and give rise to illness.
Similar to Western medicine, TCM also holds that the body has its own disease defense ability due to the existence of healthy energy (zheng qi). In chapter 72 of Suwen (The Book of Plain Questions), it states: "When healthy energy is well stored inside the body, no evils can cause interference." In chapter 33 it states: "Whenever the evils are gathered inside, a deficiency of healthy energy must be present." These statements imply that healthy energy is the body's natural resistance against disease, and disease is seen as the result of the disharmonious healthy energy within us. Occasionally, other TCM terms such as primordial qi, genuine qi or protective qi also refer to this kind of resistance. All of these embody the body's comprehensive immune functioning.
Immune modulation effects are an important part of immune functioning.
TCM holds that when healthy energy (zheng qi) is abundant, evil forces cannot prevail. According to the yin yang theory, the body's yin and yang are regulated and adjusted continuously. Keeping yin and yang in equilibrium is an essential factor to carry on normal life activities. Once this equilibrium is disturbed, disease will result.
Resuming yin and yang harmony is the universal treatment goal of TCM. The overall therapeutic strategy is to replenish deficiencies and remove excesses of yin or yang. The approaches are usually focused on holistic regulation and possession of dual modulation effects, which as stated above, are to remove excesses and replenish deficiencies. These characteristics are similar to Western medicine's understanding of our body's immune modulation effects. The dual modulation (or immune modulation) effects of TCM have the following characteristics.
| TCM focuses on mobilizing our own innate healing power; most of its remedies work on the whole being, not just on specific systems. Their healing power is far beyong the physical level; they can also work on the level of qi (vital energy) that empowers us. Even when the body seems healthy and there are no outward symptoms, immune function can be affected with symptoms present internally. Herbal remedies can find and fix these imbalances even when they are not obvious to us. | |
| To support the balancing process, TCM uses different modulation methods, for example adjusting the body's yin and yang, qi (vital energy), blood or organ functions. They can rehabilitate the body to go from a hyper-functioning state to a normal state or from an under-functioning level back to a normal state. TCM has unique theories about this, categorizing the regulating properties into four actions; "to depress when stimulated", "to rise when collapsed", "to subdue when overwhelming" and "to nourish when deficient." | |
| In some ways, normal immune functions are enhanced and the internal pathogenic factors are eliminated with dual modulation effects. A complementary relationship is formed that reinforces healthy energy and repels evils. |
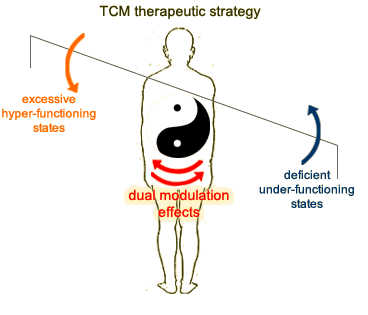 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TCM therapeutic methods are usually focused on holistic regulation and possession of dual modulation effects. The Modulation Effect of Chinese Medicines According to the concept of immunology, no matter if the immune reaction belongs to physiological or pathological factors, all the developing factors are crucial to disease formation. The basic rule for curing immune diseases is to shift the pathological immune reaction to a normal physiological immune reaction. In TCM, it is expressed by regulating the yin and yang balance, by applying holistic approaches to enhance the system's harmony, a method called dual modulation. Certainly, the immune modulation effect of Chinese medicine is extremely complicated, only a preliminary understanding has been revealed at this moment. Below are a few areas of discovery. Modern research shows that the majority of individuals suffer from syndromes of deficiency, various degrees of under-functioning or a disturbance of their immune system. Correspondingly, most of the tonifying herbs applied to these conditions can enhance immune function. For example, herbs like Lingzhi, ginseng, Tang shen, milk vetch root (huang qi), large head artactylodes rhizome (bai zhu), deer antler and Chinese caterpillar fungus, Chinese angelica (dang gui) and Barbary wolfberry fruit (gou qi zi) enhance the engulfing activities of monocytes, promote T- lymph cells' activation, increase the NK cells' activation and specific antibody productions and induce interferon reactions. Tonifying herbs that are blood builders like Barbary wolfberry fruit (qi zi), fleece flower root (shou wu), donkey hide glue, rehmannia root (di huang), Chinese angelica (dang gui) and deer antler enhance blood production in the bone marrow (immune organ) significantly. They can be used as adjuvant therapy in leucopenia (low level of white blood cells) conditions caused by radio or chemotherapies, or some autoimmune blood diseases.
In the herbal category for heat clearing, many herbs promote immune function or the body resistance. Meanwhile, they also inhibit certain adverse immune reactions that are harmful to the body. For example, herbs like Baical skullcap root (huang qin), honeysuckle flower (jin yin hua), wormwood (qing hao) and Trichosanthes root (tian hua fen) inhibit hypersensitivity significantly. Some of them also induce the production of interferon or tumor necrosis factor. Enhancement of the pituitary- adrenal cortex can also be done with this category of herbs such as Spreading hydyotis (bai hua she she cao), Ningpo fogwort (xuan shen), Andrographis (chuan xin lian) and Northern ash bark (qin pi).
Besides the benefit of improving the cardiovascular system and dynamic blood activities, some herbs used for blood and circulation also possess important effects on immune regulation. Herbs like notoginseng, achyranthes (niu xi), Dan shen, Szechuan Lovage (Chuan xiong), peach kernel (tao ren) and Argy wormwood leaf (ai ye) increase T-lymph cells and promote specific antibody production. Some other herbs like notoginseng and madder (qian cao) promote blood production in the bone marrow too.
Main effect of herbs in the category for expelling wind and relieving syndromes of exterior type, are on the body's immune barriers, such as skin, respiratory mucosa, or localized body fluids and cell immune functioning. For example, some of them enhance the engulfing actions of phagocytes, like Divaricate Saposhnikovia root (fangfeng), cassia twig, Perilla leaf (su ye), fresh ginger and Chinese tororwax root (chai hu). However, some herbs also act directly on the immune organs.
It is well known that Chinese drugs used for rheumatism possess significant immune inhibiting effects. Herbs used to treat this condition include Oriental vine stem (qing feng teng), Tripterygium (lei gong teng) and Northern fangji (Radix Stephaniae Tetrandrae). Other herbs that inhibit multiple hypersensitivity reactions are Paniculate Swallowwort root (xu chang qing), Slenderstyle Acanthopanax bark (wu jia pi) and Largeleaf gentian root (qin jiao).
Chinese herbs that possess anti-cancer effects can depress or kill cancer cells by inducing certain immune actions. Such herbs are natural indigo, Java Brucea fruit (ya dan zi), sweet melon pedicel and Chinese fir. Some of these herbs even boost the overall immune functions, such as toad venom, Java Brucea fruit (ya dan zi), blister beetle (ban mao), natural indigo and sweet melon pedicel. Also, some herbs like garlic can help reduce carcinogenic factors. Most Chinese medicines are natural substances that remain in their natural form when used for treatment. After being tested and verified for thousand years by Chinese medicine practitioners, those left behind have proven their effects. Scientists have noted multiple efficacies of these prescriptions which have dual modulation and adaptive capabilities. However, even in the study of immune modulation, projects for Chinese medicine are huge and complex, and the current overall research work has not been systematic. Among those single herbs or formulas, it is necessary to carry out more in depth investigations for further explanation about the mechanism of how these herbal ingredients work. |





















No comments:
Post a Comment